
Creation Vs Writing
Creation Vs Writing
Content creation refers to the process of producing and distributing information or media for a specific audience. This content can take various forms, including written articles, blog posts, videos, images, infographics, podcasts, and more. The goal of content creation is to engage and provide value to the target audience, whether for entertainment, education, information, or promotion.
Content writing is the process of creating written material for various purposes, primarily for online consumption. Content writers are responsible for producing text-based content that is engaging, informative, and tailored to the intended audience. The goal of content writing can vary depending on the context, but common objectives include providing information, educating, entertaining, or promoting a product or service.
What are the key steps of Content Creation?
Content creation involves several key steps:
- Ideation: Generating ideas for content based on audience interests, current trends, or specific goals. Ideation refers to the process of generating, developing, and brainstorming creative ideas. It is a critical phase in various fields, including business, design, marketing, problem-solving, and innovation. The goal of ideation is to produce a diverse range of ideas that can be explored, refined, and implemented aspects of ideation include:
- Creativity: Ideation involves thinking outside the box and coming up with innovative solutions or concepts. It encourages a creative mindset that allows for unconventional and original ideas to emerge.
- Open-mindedness: Participants in the ideation process should be open-minded and receptive to a wide range of ideas. This helps create an environment where everyone feels free to contribute without fear of judgment.
- Collaboration: Ideation often benefits from collaboration, as diverse perspectives and experiences can lead to more comprehensive and unique ideas. Group brainstorming sessions are common in collaborative ideation processes.
- Problem-solving: Ideation is frequently used in problem-solving contexts, where individuals or teams work together to generate solutions for challenges or opportunities.
- Exploration: The process involves exploring various angles, possibilities, and scenarios. It’s not about settling on the first idea but rather exploring multiple options before narrowing down to the most promising ones.
- Visual Tools: Some creation sessions make use of visual tools, such as mind maps, mood boards, or sketches, to help participants express and organize their ideas visually.
- Iteration: Creation is an iterative process, meaning that ideas can be revisited, refined, and combined to create stronger, more viable concepts.
- Timed Sessions: In some cases, ideation sessions are structured with time constraints to encourage quick thinking and prevent overthinking.
- Planning: Creation of a content strategy that outlines the goals, target audience, channels for distribution, and a publishing schedule. Planning is the process of outlining and organising tasks, activities, or strategies to achieve specific goals or objectives. It involves setting objectives, determining the steps needed to accomplish those objectives, allocating resources, and establishing timelines. Planning is a fundamental aspect of various areas of life, including business, education, project management, personal development, and more.
Key components of planning include:- Goal Setting: Clearly defining the desired outcomes or objectives is the starting point of planning. Goals provide direction and purpose, guiding the planning process.
- Identifying Resources: Determining the resources required, such as personnel, finances, materials, and technology, is crucial for effective planning. Resource allocation ensures that the necessary tools and support are available.
- Creating a Timeline: Establishing a timeline or schedule helps in organizing tasks and setting deadlines. It provides a framework for tracking progress and staying on course.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential challenges or risks allows for proactive measures to be incorporated into the plan. This helps in mitigating potential issues that may arise during the execution phase.
- Task Allocation: Assigning responsibilities to individuals or teams ensures that everyone understands their role in the plan. This promotes collaboration and accountability.
- Budgeting: For business or project planning, budgeting involves estimating and allocating financial resources to cover expenses. It helps in managing costs and ensuring financial sustainability.
- Adaptability: Plans should be flexible enough to adapt to changing circumstances or unexpected events. This involves considering alternative courses of action in case the original plan needs adjustments.
- Communication: Effective communication is vital to ensure that all stakeholders are informed about the plan, their roles, and any changes that may occur. This fosters collaboration and alignment.
Examples of planning in various contexts include:
- Business Planning: Developing strategies and action plans to achieve business goals.
- Project Planning: Organizing tasks, allocating resources, and setting timelines for project completion.
- Educational Planning: Creating lesson plans or curriculum outlines for teaching purposes.
- Personal Planning: Setting personal goals, creating schedules, and making long-term plans for personal development.
Overall, planning is a proactive and systematic process that enhances the likelihood of success by providing structure and direction to endeavours.
- Creation: Producing the actual content, whether it’s writing articles, recording videos, designing graphics, or other forms of media.
“Creation” generally refers to the act of bringing something into existence or forming something new. It can encompass a wide range of activities across various domains, including art, literature, science, technology, and more. The term is often associated with the creative process and the generation of something that did not previously exist.
Key aspects of creation include:- Innovation: Creation often involves introducing new ideas, concepts, or inventions that contribute to progress and development in a particular field.
- Expression: In artistic and creative contexts, creation is a means of expressing thoughts, emotions, or imagination through various mediums such as writing, visual arts, music, and more.
- Procreation: In a biological context, creation can refer to the process of producing offspring or new life.
- Invention: Creating something can involve the development of new technologies, products, or solutions to problems, contributing to advancements in various industries.
- Imagination: The act of creation often begins with imagination—a cognitive process that involves forming new ideas or mental images.
- Design: In fields like graphic design, architecture, and product development, creation involves the intentional design of aesthetically pleasing and functional entities.
- Building: Creation can involve physically constructing or assembling something, such as buildings, structures, or machines.
Artistic Expression: Artists engage in the creation of paintings, sculptures, literature, films, and other forms of art to communicate ideas and evoke emotions.
- Editing: Reviewing and refining the content to ensure quality, accuracy, and consistency with the brand or message. Editing is the process of reviewing, revising, and refining content to improve its overall quality, coherence, and effectiveness. It involves carefully examining written or visual material and making adjustments to enhance clarity, style, grammar, and overall presentation. Editing is a crucial step in the content creation process and can be applied to various forms of media, including written articles, documents, videos, and images aspects of the editing process include:
-
- Grammar and Syntax: Editors check for grammatical errors, punctuation, and proper sentence structure. This ensures that the language is clear, correct, and adheres to the appropriate style guide.
- Style and Consistency: Editors maintain consistency in writing style, tone, and formatting throughout the content. They may also ensure that the content aligns with established brand guidelines or industry standards.
- Clarity and Coherence: Editors work to improve the overall flow and coherence of the content. They may rearrange sentences or paragraphs, eliminate redundancies, and ensure that the content is easy to understand.
- Content Structure: Editors assess the organisation and structure of the content, making adjustments to improve the logical flow of ideas. This may involve reordering sections, adding transitions, or rephrasing sentences.
- Fact-Checking: In non-fiction content, editors verify the accuracy of information and ensure that statements are supported by reliable sources. Fact-checking is particularly important for maintaining the credibility of the content.
- Tone and Voice: Editors pay attention to the tone and voice of the content, ensuring that it aligns with the intended audience and purpose. They may adjust language to achieve the desired emotional or persuasive effect.
- Formatting and Layout: In addition to text-based editing, editors may address formatting issues, ensuring that the content is visually appealing and easy to read. This can include adjustments to fonts, spacing, and overall layout.
- Feedback and Collaboration: In collaborative settings, editors provide constructive feedback to the content creators. This collaborative approach helps refine the content and ensures that it meets the intended goals.
- Optimization: Tailoring the content creation for different platforms and optimising it for search engines (SEO) to increase visibility. Key aspects of optimization include:
- Performance Improvement: The primary goal of optimization is to improve the performance of a system, process, or entity. This could involve enhancing efficiency, speed, accuracy, or overall effectiveness.
- Resource Utilisation: Optimization often focuses on maximising the use of available resources, whether it be time, money, personnel, or other assets. It aims to achieve the best possible outcome with the given resources.
- Problem-solving: Optimization is frequently used to address problems or challenges by finding the most efficient and effective solutions. This can involve minimising costs, maximising profits, or achieving specific objectives.
- Algorithmic Optimization: In computer science, optimization involves improving the efficiency of algorithms, code, or software to reduce execution time, memory usage, or other performance metrics.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): In the context of online content, SEO refers to optimising web content to improve its visibility on search engines. This includes using relevant keywords, creating high-quality content, and ensuring a website’s structure is search engine-friendly.
- Process Optimization: Businesses often optimise their operational processes to streamline workflows, reduce bottlenecks, and enhance overall efficiency. This can lead to cost savings and improved productivity.
- Supply Chain Optimization: In logistics and supply chain management, optimization aims to enhance the movement of goods, reduce transportation costs, minimise inventory levels, and improve overall supply chain performance.
- Parameter Tuning: In various scientific and engineering applications, optimization involves adjusting parameters to achieve the best possible results. This is common in fields like machine learning, where algorithms are fine-tuned to improve predictive accuracy.

Be Creative
Distribution: Sharing the content creation through various channels such as websites, social media, email newsletters, and more. Key aspects of distribution include:
-
- Channels: Distribution channels are the paths through which products or services move from the manufacturer or provider to the end-user. These can include direct sales, wholesalers, retailers, distributors, e-commerce platforms, and more.
- Logistics: The physical movement and transportation of goods are integral to distribution. This involves coordinating shipping, warehousing, inventory management, and other logistical activities to ensure timely delivery.
- Retail: In the context of consumer goods, distribution often involves selling products through retail outlets. This can include brick-and-mortar stores, online retailers, and other points of sale.
- Wholesaling: Distributors may sell products in large quantities to wholesalers, who, in turn, sell them to retailers or other businesses. This can help streamline the supply chain and reach a broader market.
- E-commerce: With the growth of online shopping, distribution has evolved to include digital channels. E-commerce platforms enable direct sales to consumers, bypassing traditional retail channels.
- Marketing and Promotion: Distribution strategies are often closely tied to marketing and promotional efforts. The goal is to create awareness, generate demand, and facilitate the purchase of products or services.
- Supply Chain Management: Distribution is a key element of supply chain management, which involves the entire process of producing, transporting, and delivering goods to consumers. Efficient supply chain management contributes to cost savings and customer satisfaction.
- Global Distribution: In a globalized economy, distribution may involve international trade and shipping. Companies may use various strategies, such as establishing distribution center’s in different regions or partnering with local distributors, to reach a global audience.
- Analysis: Monitoring the performance of the content through analytics, gathering insights on audience engagement, and adjusting strategies accordingly. Analysis is the process of breaking down a complex topic or substance into smaller parts to gain a better understanding of it. It involves examining the components, relationships, and underlying principles to discern patterns, trends, and insights. Analysis is employed across various disciplines, including science, mathematics, business, literature, and more, with the goal of extracting meaningful information and drawing conclusions. Key aspects of analysis include:
- Data Examination: In fields like science and statistics, analysis involves the examination of data to identify patterns and trends. This can include statistical analysis, data visualization, and other techniques to derive insights.
- Problem Solving: Analysis is often used as a problem-solving tool, breaking down complex issues into manageable components. By understanding the underlying factors, individuals or teams can develop effective solutions.
- Critical Thinking: Analysis encourages critical thinking, which involves evaluating information, considering different perspectives, and making informed judgments. It helps in discerning the reliability and validity of data.
- Literary Analysis: In literature, analysis involves examining elements such as plot, character development, themes, and symbolism to gain a deeper understanding of a literary work.
- Business Analysis: In the business context, analysis is used to assess market trends, financial performance, and operational efficiency. Business analysts may examine data to make recommendations for strategic decision-making.
- Scientific Research: Scientific analysis involves the examination of experimental data and results to draw conclusions about the natural world. This process is integral to the scientific method.
- Textual Analysis: In linguistics and literature, textual analysis involves examining written or spoken language to understand its structure, meaning, and context.
- Financial Analysis: Financial analysts assess financial statements, market trends, and economic indicators to provide insights into the financial health of a company or industry.
The concept of creation is broad and can be applied in diverse contexts, reflecting the human capacity for innovation, expression, and the generation of new entities or concepts. Whether in the arts, sciences, or daily life, creation plays a fundamental role in shaping the world around us.
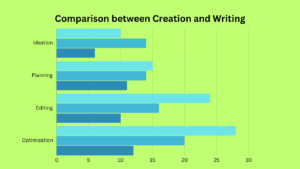
Creation Vs Writing
What are the key steps of Content Writing?
Here are some key aspects of content writing:
Audience Understanding: Content writers need to have a clear understanding of their target audience. Knowing the demographics, interests, and preferences of the audience helps in creating content that resonates with them. Content writing plays a crucial role in audience understanding by creating and delivering information in a way that resonates with the target audience. Here are several ways in which content writing contributes to audience understanding:
- Clear and Concise Communication:
- Content writers strive to present information in a clear and concise manner. This helps the audience grasp key concepts without being overwhelmed by unnecessary details.
- Adaptation to Audience Level:
- Good content writers tailor their writing style and language to the level of their target audience. Whether the audience is composed of experts in a field or beginners, the content is adjusted to meet their comprehension level.
- Use of Audience-Relevant Examples:
- Content writers often use relatable examples or analogies that resonate with the experiences and interests of the target audience. This helps in making complex ideas more understandable.
- Addressing Audience Needs and Concerns:
- Content writing involves understanding the needs, concerns, and questions of the audience. By addressing these directly, content writers can provide valuable information and build a connection with the readers.
- Engaging and Maintaining Interest:
- Engaging content keeps the audience interested and encourages them to continue reading. This is achieved through compelling storytelling, relevant anecdotes, or any method that captures and maintains the audience’s attention.
- Incorporating Visual Elements:
- Including visual elements like images, infographics, and charts can enhance audience understanding. Visual aids can simplify complex information and make it more digestible for various learning preferences.
- Consistent Brand Voice:
- Establishing a consistent brand voice in content helps create a familiar and recognizable communication style. This consistency contributes to building a relationship of trust with the audience.
- Feedback and Iteration:
- Content writers often review audience feedback and analytics to understand how well their content is resonating. This iterative process allows for adjustments and improvements to better cater to the audience’s preferences and needs.
- Clarity in Call-to-Action (CTA):
- Content often includes a call-to-action, prompting the audience to take a specific step. Clear and well-crafted CTAs contribute to audience understanding of what is expected from them.
- Cultural Sensitivity:
- Understanding the cultural context of the audience is vital. Content writers need to be sensitive to cultural nuances to ensure that the content is relevant and respectful to diverse audiences.
Clarity and Conciseness: Good content is clear, concise, and easy to understand. Content writers strive to convey information in a straightforward manner, avoiding unnecessary jargon or complexity. Here’s how content writing contributes to clarity and conciseness:
- Clear Language and Structure:
- Precise Vocabulary: Content writers choose words carefully to convey the intended meaning without ambiguity. This helps in eliminating confusion and promoting clarity.
- Logical Organisation: Well-structured content with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion enhances readability and aids comprehension.
- Avoidance of Jargon and Complexity:
- Simplified Language: Content writers often strive to explain complex concepts using simple and straightforward language. This helps a diverse audience understand the content easily.
- Minimization of Jargon: Unnecessary technical terms or jargon are avoided or explained to prevent confusion among readers who may not be familiar with specialised terminology.
- Concise Expression of Ideas:
- Elimination of Redundancy: Content writers aim to convey information without unnecessary repetition. Redundancies are removed to maintain a concise and focused message.
- Avoidance of Wordiness: Unnecessary filler words or phrases are omitted, ensuring that each sentence contributes directly to the message. This prevents the content from becoming verbose.
- Clarity in Sentence Structure:
- Active Voice: The use of active voice helps in clearly identifying the subject and the action, making sentences more direct and easy to understand.
- Clear Pronoun Reference: Writers pay attention to pronoun use to avoid confusion about the referent, ensuring clarity in the communication.
- Use of Visual Elements:
- Headings and Subheadings: Breaking down content into clear headings and subheadings helps readers navigate the material and understand the organisation of the information.
- Bullet Points and Lists: Lists and bullet points are effective in presenting information concisely, making it easy for readers to grasp key points.
- Audience-Centric Approach:
- Understanding the Audience: Content writers consider the needs, background, and interests of the target audience. Tailoring the content to the audience enhances clarity and relevance.
- Addressing Questions: Anticipating potential questions readers may have and addressing them in the content contributes to clarity by providing comprehensive information.
- Proofreading and Editing:
- Error-Free Content: Thorough proofreading and editing help in eliminating grammatical errors, typos, and other issues that could hinder clarity. Well-edited content enhances overall quality.
SEO Optimization: Content writers often incorporate search engine optimization (SEO) techniques to make their content more discoverable by search engines. This involves using relevant keywords, structuring content properly, and following SEO best practices. Effective content writing helps improve SEO in several ways:
- Relevant Keywords: Content writers strategically incorporate relevant keywords into the content. These keywords are terms that users are likely to search for when looking for information on a particular topic. Proper keyword usage helps search engines understand the context and relevance of the content.
- Quality Content: Search engines, especially Google, prioritize high-quality, valuable content. Well-written and informative content tends to attract more visitors and encourages them to stay on a webpage longer. Search engines interpret this as a positive user experience, which can contribute to higher rankings.
- User Intent: Content writers focus on understanding user intent and creating content that directly addresses the needs and queries of the target audience. By aligning content with user intent, websites are more likely to rank well for relevant search queries.
- Optimised Headings and Structure: Content writers use optimised headings and a clear content structure to make it easier for both users and search engines to understand the hierarchy of information on a page. Proper formatting enhances readability and helps search engines index the content accurately.
- Internal and External Linking: Content often includes internal links to other relevant pages within the same website, and external links to reputable sources. This not only enhances the user experience but also provides search engines with additional context and signals about the content’s credibility.
- Regular Updates: Regularly updating website content with fresh and relevant information signals to search engines that the website is active and current. This can positively impact search engine rankings.
- Mobile-Friendly Content: With the increasing use of mobile devices, search engines prioritise mobile-friendly websites. Content writers ensure that content is optimised for mobile devices, improving the overall user experience and positively influencing SEO.
- Social Signals: Well-crafted content is more likely to be shared on social media platforms. Social signals, such as likes, shares, and comments, can indirectly contribute to SEO by increasing the visibility and authority of the content.
- Rich Media Integration: Content writers may incorporate rich media, such as images, videos, and infographics, which not only enhances the user experience but also provides additional opportunities for optimization. Properly optimised media files can contribute to better search engine rankings.
Creativity: While some content may require a more formal tone, creativity is often essential to keep the audience engaged. This can involve storytelling, using compelling language, and incorporating elements that capture attention Content writing and creativity are closely intertwined, and content writing can significantly enhance and showcase creative expression. Here’s how content writing helps foster creativity:
- Expression of Ideas: Content writing provides a platform for individuals to express their ideas, thoughts, and emotions. Whether it’s through storytelling, poetry, or informative articles, writers can use language creatively to convey their unique perspectives.
- Exploration of Themes and Topics: Content writing allows writers to explore a wide range of themes and topics. This exploration encourages creative thinking and the generation of innovative ideas as writers delve into different subjects and perspectives.
- Development of a Unique Voice: Through content writing, individuals can develop and refine their unique voice and style. This process involves experimenting with language, tone, and narrative techniques, fostering creativity in the way ideas are presented.
- Creative Problem-Solving: Content writing often involves addressing challenges, whether it’s finding the right words, structuring a piece effectively, or conveying complex information in a simple manner. This problem-solving aspect of writing nurtures creative thinking and adaptability.
- Imagination and Storytelling: Writing allows for the use of imagination and storytelling. Writers can create fictional worlds, characters, and narratives, unleashing their creativity to captivate and engage readers.
- Innovation in Communication: Content writing encourages writers to innovate in how they communicate ideas. This might involve experimenting with new formats, incorporating multimedia elements, or adopting unconventional styles to capture and maintain audience attention.
- Collaboration and Idea Sharing: Content writing often involves collaboration, such as brainstorming ideas with others or seeking feedback from peers. This collaborative process can spark new ideas, fuel creativity, and provide fresh perspectives.
- Adaptation to Different Styles: Depending on the content’s purpose and audience, writers may need to adapt their writing style. This flexibility challenges writers to think creatively about how to convey information effectively while maintaining their unique voice.
- Inspiration from Diverse Sources: Content writers often draw inspiration from diverse sources, including literature, art, science, and everyday experiences. This exposure to various influences can fuel creativity by connecting seemingly unrelated concepts.
- Continuous Learning: Content writing involves continuous learning and research, especially when covering new topics. This constant exploration of information stimulates creativity and broadens the writer’s knowledge base.
Adaptability: Content writers may need to adapt their writing style to different platforms, such as blogs, social media, or product descriptions. Each platform may have its own conventions and requirements. A content writer who demonstrates adaptability can effectively create content that resonates with diverse audiences and meets the requirements of various contexts. Here’s how content writing is connected to adaptability:
- Audience Understanding:
- Adapting Tone and Style: Different audiences may respond better to varying tones and styles of writing. An adaptable content writer can adjust the tone and style to suit the preferences and expectations of the target audience.
- Content Formats and Platforms:
- Versatility in Formats: Content writers often need to create content for different platforms and formats, such as blog posts, social media, email newsletters, or product descriptions. Adaptable writers can switch seamlessly between these formats, understanding the nuances and requirements of each.
- Industry Knowledge:
- Acquiring New Knowledge: Content writers may need to create content for diverse industries. Being adaptable involves quickly acquiring the necessary knowledge about a new industry, understanding its terminology, trends, and audience expectations.
- Changing Trends:
- Staying Current: Adaptability in content writing requires staying abreast of changing trends in the industry and adjusting content strategies accordingly. This may involve incorporating new technologies, responding to shifts in consumer behaviour, or embracing emerging content formats.
- SEO Practices:
- Adjusting to Algorithm Changes: Search engine algorithms frequently evolve, impacting the visibility of content. An adaptable content writer understands SEO best practices and can adjust their writing to align with changes in search engine algorithms.
- Client or Brand Guidelines:
- Aligning with Brand Voice: Content writers often work with different clients or brands, each with its unique voice and guidelines. An adaptable writer can quickly understand and align with a brand’s voice, ensuring consistency across different projects.
- Revisions and Feedback:
- Incorporating Feedback: Adaptable content writers are open to feedback and can revise their work based on client or editorial input. They understand that revisions are a normal part of the writing process and are willing to make necessary adjustments.
- Cultural Sensitivity:
- Adapting to Cultural Differences: When creating content for a global audience, cultural sensitivity is crucial. Adaptable content writers can tailor their content to respect cultural differences, ensuring it is relevant and respectful in diverse regions.
Research Skills: Depending on the topic, content writers may need to conduct research to ensure accuracy and provide valuable information to their audience. Research skills are crucial for producing high-quality content. Research skills play a crucial role in content writing, contributing to the creation of well-informed, credible, and engaging content. Here are several ways in which research skills benefit content writing:
- Accuracy and Credibility: Research skills help content writers gather accurate and reliable information. This ensures that the content is trustworthy and credible, which is essential for building the audience’s trust.
- In-depth Understanding: Thorough research allows content writers to gain a deeper understanding of the topic they are writing about. This depth of knowledge is reflected in the content and helps writers provide valuable insights and analysis.
- Topic Exploration: Research skills enable writers to explore various aspects of a topic, uncovering different perspectives, trends, and relevant data. This exploration adds richness and diversity to the content, making it more comprehensive.
- Supporting Evidence: Research helps content writers find supporting evidence and examples to strengthen their arguments or points. Including data, statistics, and real-world examples adds weight to the content and enhances its persuasiveness.
- Keyword Optimization: For online content, research skills are crucial for identifying relevant keywords. Incorporating these keywords strategically can improve the content’s search engine visibility, making it more likely to reach the target audience.
- Staying Updated: Content writers need to stay current with industry trends, news, and developments. Research skills help writers keep their content fresh and relevant, ensuring that it reflects the latest information.
- Audience Understanding: Researching the target audience allows content writers to tailor their content to meet the needs and interests of the readers. Understanding the audience’s preferences and pain points helps in creating more resonant and engaging content.
- Avoiding Plagiarism: Research skills help writers avoid unintentional plagiarism by ensuring they attribute information correctly. Proper citation and referencing are essential for maintaining the integrity of the content.
- Content Variety: Research skills enable writers to explore different formats, styles, and tones of content. Whether it’s a blog post, whitepaper, infographic, or video script, the ability to research and adapt is crucial for creating diverse and appealing content.
- Identifying Trends: Content that reflects current trends and emerging topics tends to attract more attention. Research skills allow content writers to identify and incorporate relevant trends into their work, keeping the content timely and engaging.
Editing and Proofreading: Editing and proofreading are crucial steps in the content writing process, playing a significant role in ensuring the quality, clarity, and professionalism of written materials. While they are distinct processes, they both contribute to refining and polishing content before it is published or presented to an audience.
- Clarity and Readability:
- Editing: In the editing phase, content is reviewed for overall clarity, coherence, and structure. Sentences and paragraphs may be rephrased for better flow, and transitions between ideas are improved.
- Proofreading: Proofreading focuses on surface-level issues like grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Ensuring that the text is free from errors contributes to a smooth reading experience.
- Grammar and Language Accuracy:
- Editing: Editors check for grammatical correctness, appropriate language usage, and adherence to style guides. They may address issues related to syntax, tense, and sentence construction.
- Proofreading: Proofreaders specifically focus on identifying and correcting errors in grammar, spelling, punctuation, and typographical mistakes.
- Consistency:
- Editing: Editors ensure consistency in tone, style, and formatting throughout the content. They also check for consistency in terminology and the use of brand-specific language.
- Proofreading: Proofreaders catch inconsistencies in spelling, punctuation, and formatting, making sure that the document adheres to a consistent and professional standard.
- Audience Engagement:
- Editing: Editors assess whether the content is engaging and meets the needs of the target audience. They may suggest adjustments to improve the overall impact of the message.
- Proofreading: While proofreading doesn’t directly address engagement, error-free content contributes to a positive reader experience and can enhance the credibility of the author or brand.
- Professionalism:
- Editing: Editing adds a professional touch to the content by refining language, structure, and overall presentation. It ensures that the content aligns with the intended purpose and meets high-quality standards.
- Proofreading: Proofreading enhances the professional appearance of the content by eliminating distracting errors, showcasing attention to detail.
- Editing: A well-edited piece of content reflects positively on the brand or author, contributing to a strong and consistent brand image.
- Proofreading: Error-free content is crucial for maintaining a professional brand image, as typos and grammatical mistakes can detract from credibility.
Examples of content writing include blog posts, articles, product descriptions, social media posts, newsletters, and more. It plays a crucial role in digital marketing and online communication, helping businesses and individuals connect with their target audience through written content. strong research skills empower content writers to produce high-quality, well-supported, and relevant content. The ability to gather and analyze information effectively is a foundational element of successful content creation.
FAQ
- What is content creation?
- Answer: Content creation is the process of producing and distributing information or media for a specific audience, encompassing various forms such as articles, videos, images, and more.
- What is the difference between content writing and content creation?
- Answer: Content writing is a specific aspect of content creation that focuses on producing written material, including articles, blog posts, and other textual content.
- Can you provide examples of optimization in content creation?
- Answer: Examples of optimization in content creation include using SEO techniques, adapting content for different platforms, and streamlining processes to enhance efficiency.
See the next BLOG….

